Klon Centaur circuit analysis
Summary
- Klone centaur build (Aion refractor)
- Klon centaur circuit analysis
- Klon centaur mods and tweaks
- Klon centaur history and versions
For those who do not know the Klon Centaur yet, it is an overdrive created in the 90s by Bill Finnegan and MIT engineers (yes!), that is probably the "hypest" pedals of all. It was used by many guitarists, including Jeff Beck for instance. It is a three potentiometers overdrive: gain, volume and trebles, famous for the light crunchy tones it provides to your sound. It has also an excellent reputation as a buffer or clean boost. In fact, I have already made Klon buffer PCBs to use it in a patch box.
The Klon is a rather complex circuit. It is quite weird because there are lots of informations and tests about this pedal online, however there are few informations about how the circuit works precisely. I have to remind you that the circuit was mainly conceived by electronics engineers from the MIT (and not by Bill Finnegan, who tweaked it more than conceive it), and thus, the circuit is quite "non-standard" compared to classic overdrive circuits (Tube Screamer, Rat Distorsion...etc). So brace yourself,
If you are not very familiar with the different components, and the theory around guitar pedals, I suggest that you read a few articles about theory and other circuit analysis before reading this one!
Here is the famous circuit:
You can already see that, contrary to many overpriced "bouteeek" pedals, the circuit is not a tubescreamer, and is entirely original!
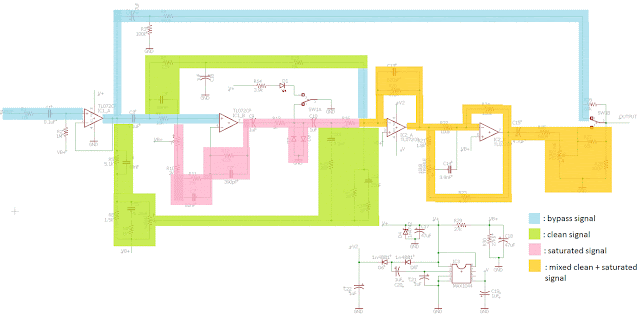
So we can already see 4 operational amplifiers (OP amps), the famous germanium diodes between the second and third OP amp. If we try to see where the signal goes, we can see that there are several pathes that the signal follows, we can see that the signal is divided between clean and saturated, and then mixed again. When the pedal is "off", the signal still goes through the top part of the circuit.
I traced the path followed by the signal:
We can see that the bypass signal (blue) is splitted in two: clean and saturated signal (green and pink, respectively). The amount of each splitted signal is dosed by a double potentiometer, the gain potentiometer. So basically, drive and clean signal are mixed, which allows really light and low saturation mimicking an amplifier just at the break up. If the Klon is so good with light drives, it is surely thanks to this mechanism that allow to have very slight saturations mixed with your clean signal.
You can also see that when the pedal is off, your signal can still go through an OP amp (it is the blue loop at the top of the schematic)... It is the famous buffer!
If we divide the circuit in different sections like we are used to, it can be this:
Finally, in the bottom right corner, you can see a power supply section using a MAX1044, that allows to have different tensions in the circuit. If you remember, the MAX1044 integrated circuits can be use to double a tension, or to invert it. Here, both of these functions are used!
Lets see this part of the circuit first!
 V+ (9V) is stabilized using a 47uF capacitor, and a diode (D4) prevents polarity inversion. It is the classical power supply scheme.
V+ (9V) is stabilized using a 47uF capacitor, and a diode (D4) prevents polarity inversion. It is the classical power supply scheme.
V+ is then divided by two using a voltage divider with R29 and R30, to have VB+ (4.5V). If you do not know what a voltage divider is, read my post about resistors and their role in effect pedals. This tension is also stabilized with a 47uF capacitor (C18).
So we can already see 4 operational amplifiers (OP amps), the famous germanium diodes between the second and third OP amp. If we try to see where the signal goes, we can see that there are several pathes that the signal follows, we can see that the signal is divided between clean and saturated, and then mixed again. When the pedal is "off", the signal still goes through the top part of the circuit.
I traced the path followed by the signal:
We can see that the bypass signal (blue) is splitted in two: clean and saturated signal (green and pink, respectively). The amount of each splitted signal is dosed by a double potentiometer, the gain potentiometer. So basically, drive and clean signal are mixed, which allows really light and low saturation mimicking an amplifier just at the break up. If the Klon is so good with light drives, it is surely thanks to this mechanism that allow to have very slight saturations mixed with your clean signal.
You can also see that when the pedal is off, your signal can still go through an OP amp (it is the blue loop at the top of the schematic)... It is the famous buffer!
If we divide the circuit in different sections like we are used to, it can be this:
Finally, in the bottom right corner, you can see a power supply section using a MAX1044, that allows to have different tensions in the circuit. If you remember, the MAX1044 integrated circuits can be use to double a tension, or to invert it. Here, both of these functions are used!
Lets see this part of the circuit first!
Klon Centaur power supply
As you can see, there are no more than 4 different tensions delivered by the Klon Centaur power supply! We have V+ (9V), VB+ (4,5V), V- (-9V) and V2+ (18V)! Simple circuits are for the newbies lel!
V+ is then divided by two using a voltage divider with R29 and R30, to have VB+ (4.5V). If you do not know what a voltage divider is, read my post about resistors and their role in effect pedals. This tension is also stabilized with a 47uF capacitor (C18).
Finally, the MAX1044 is used to have an inverted tension (V-, -9V) and doubled (+V2, +18V). The MAX1044 is an integrated circuit sold by Maxim, that allows to transform tensions. Here, it is used as indicated on the datasheet (as simple as that!). For more infos about the MAX1044, read my article avec voltage doublers.
Klon buffer analysis
The blue loop on the top of the circuit that goes towards the output of the circuit is only active when the pedal is "off". It is the famous buffer! A buffer has a high input impedance, and a low output impedance, so that high frequencies are maintained all along your signal chain. Here is the scheme of the klon buffer:
The first part, until C2, is simply the circuit input. There is a resistor at the input of the circuit (R1), and a pulldown resistor to avoir "popping" noises when the circuit is turned on. For more infos about pulldown resistor, read my article about resistors in guitar pedals.
The C1 capacitor is a coupling capacitor: it prevents parasitic DC currents from the pickups to go in the circuit. With R2 resistor, it also forms a high pass filter. If the value of the capacitor is bigger, you will allow more bass to go though the circuit. Here, with a value of 0.1uF, most of the bass of the guitar will go through the buffer, so the buffer will be transparent!
Then, the signal enters the OP amp, first one of the TL072CP. The TL072 is a double OP amp, very transparent. It is wired in non inverter (signal enters the OP amp through the + input). Usually, they are some resistors to define the gain of the amplifier, here, there are none. Thus, the gain is around 1, which allows you to have the same volume at the input, and the output. The OP amp has a high impedance input, and a low impedance output: the buffer diminishes the signal impendance, and maintains the volume!
Finally, there is a 4.7uF coupling cap, combined with a 100k resistor connected to the ground. This is a high pass filter (again), that will let almost all bass frequencies go through it (again). A last 560R resistor will adjust the final volume, and the signal gets out of the buffer.
Signal splitter
When the circuit is "on", the signal does not goes through the buffer, that is disconnected from the circuit by the footswitch, but through a "splitter". This part of the circuit splits the signal in two: clean and saturated signal.At the input of the splitter, there is the beginning of the buffer circuit. Instead of going to the top partof the circuit, the signal can now take several pathes: down through the 5.1k resistor and the C4 capacitor, go through the second OP amp, or can go through the R17 resistor... What is this mess?
These different splitters selects some specifics frequencies. Unfortunately, I am not good enough with theory to tell you which ones... It involves rather complicated calculations with Fourier transforms and all... If any talented personn could help me with that, it would be awesome!
Lets focus on the bottom part. The signal goes through different components (R5, C4, R6, C6 and R9), then goes through the GAIN2 potentiometer, that set the maximum . You can see that the signal does not goes through any diode clipping system, so this part of the signal stays clean. In the end of the loop, it is mixed with the saturated signal.
The clean signal can also go through the top part of circuit, with the 1,5 and 15k resistor. It adds a bit of clean signal in the end that is mixed with the GAIN2 clean signal and the saturated signal, in order to always have a bit of clean mixed with the saturated signal, even when GAIN2 is maxed.
Finally, the remaining signal goes to the input of the second OP amp. A GAIN1 potentiometer set the amount of signal going into the amplification loop of the OP amp. GAIN1 and GAIN2 are in fact one double potentiometer: when the value of one increase, the other one increase! Thus, it doses the amount of clean and saturated signal to mix together: the more saturated signal, the less clean signal! It is an unique feature that is not present in any other pedal, and this is one of the novelty brung by the Klon Centaur: a part of the signal is kept as is, and the other part is saturated. Thus, the overdrive is really good for low drive.
The saturation comes mainly from the OP amp saturation. Another thing that is not usual with classic overdrives circuits! It has quit a high gain. We can calculate it. It is wired in non-inverter, so the gain will be 1 + loop resistor / resistor to ground = 1 + 422 / (15 + 2 + value of the 100k potentiometer = 1 + 422 / (117) = 4,6 with the lowest gain, and 1 + 422 / (17) = 25,8 when gain is maxed.
Then, there is a coupling capacitor (C9), and signal arrives towards the famous germanium diodes D2/D3. Most of the times, with moderate gain, these diodes are useless! I could test that with my soul food mod. They only are important when the gain is set up pretty high.
Finally, at the end of the splitter, all the signals are mixed again together.
Output signal mixer
Here we are, this is the last part of the circuit, the "signal mixer"!
A first OP amp wired in inverter amplifies the signal. This OP amp has quite a high gain, that insures a high volume gain, useful if you want to use the Klon as a boost. This is where the incredible amount of volume of the Centaur comes from.
A second OP amp with a gain of 1 (look at the values of R22 and R24) will allow to set the final amount of trebles in the output signal. It is a classical high pass filter: you let the signal go through until a certain frequency, defined by the C14 capacitor. Decreasing the value of this capacitor will let more treble go through. A common mod is to increase the value of this cap to have less treble (we will see it later). The amount of trebles that can go through this cap is set by the treble potentiometer.
Finally, a 4.7uF coupling capacitor prevents parasit DC current from going into the last section. A 560R resistor the volume potentiometer will define the final volume of the output! There are also two resistors, R27 and R28, but I have to admit that I have no clue about their role... if anyone knows?
There are still things that I do not really get with this circuit... I guess it is a little bit overcomplicated. I would love to understand the splitter in details, but I am still lacking some precious filters knowledge...
I hope it still gave you an idea about how the circuit works. If you have any question, do not hesitate to post a comment. Lets have fun now that we know the circuit: klon centaur modsand tweaks!
There it is, this is the end of this post! I know it is dense, so take your time, and do not hesitate to ask questions by posting a comment! I this point, I am not totally sure about how each part of the circuit works, so do not hesitate to correct mistakes I could have made in the circuit analysis.
Did you like this article ? Thank me by liking the Coda Effects facebook page!
To go further
2009 document produced in 2009 by Martin Chittum from freestompboxes.org
Aion electronics building guide, well helpful and with a lot of informations about the Klon Centaur.
Refractor project page by Aion Electronics.
"Klown" Centaur page of the Revolution Deux website.
"Sunking" project from madbean pedals, another Klon clone with a bigger PCB for 1590BB enclosures.
Modded "Klown" centaur of the Revolution Deux website.
Website with pictures of Klon centaur, classified by serials
Manticore fx : lots of informations about the Klon
History of the Klon Centaur on Premier Guitar, with a Bill Finnegan interview.
Klone science on madbean pedal: frequency response plots of different klon clones
Refractor project page by Aion Electronics.
"Klown" Centaur page of the Revolution Deux website.
"Sunking" project from madbean pedals, another Klon clone with a bigger PCB for 1590BB enclosures.
Modded "Klown" centaur of the Revolution Deux website.
Website with pictures of Klon centaur, classified by serials
Manticore fx : lots of informations about the Klon
History of the Klon Centaur on Premier Guitar, with a Bill Finnegan interview.
Klone science on madbean pedal: frequency response plots of different klon clones





Commentaires
Enregistrer un commentaire